what communicates with the computer and tells it what to do?
Introduction to Computers
The Big Picture
A computer organization has three main components: hardware, software, and people. The equipment associated with a computer arrangement is called hardware. Software is a gear up of instructions that tells the hardware what to do. People, still, are the nearly of import component of a estimator system - people use the power of the computer for some purpose. In fact, this class volition evidence you that the computer can be a tool for just about anyone from a concern person, to an artist, to a housekeeper, to a educatee - an incredibly powerful and flexible tool.
Software is actually a computer program. To be more specific, a program is a set of pace-by-pace instructions that directs the computer to do the tasks you want it to do and to produce the results y'all want. A estimator programmer is a person who writes programs. Most of united states of america practise not write programs, we utilise programs written past someone else. This means we are users - people who purchase and use computer software.
Hardware: Coming together the Auto
What is a calculator? A six-yr-onetime called a computer "radio, movies, and telly combined!" A ten-year-old described a computer as "a television set you can talk to." The x-year-old's definition is closer but still does not recognize the computer every bit a motorcar that has the power to make changes.A computer is a automobile that can be programmed to accept data (input), process it into useful information (output), and store it away (in a secondary storage device) for safekeeping or subsequently reuse. The processing of input to output is directed past the software but performed by the hardware.
To function, a computer arrangement requires iv main aspects of data handling: input, processing, output, and storage. The hardware responsible for these 4 areas operates as follows:
- Input devices accept data in a course that the figurer tin can apply; they then send the data to the processing unit.
- The processor, more formally known every bit the central processing unit (CPU), has the electronic circuitry that manipulates input data into the information people want. The central processing unit executes reckoner instructions that are specified in the program.
- Output devices show people the candy information-data in a grade that they can use.
- Storage usually means secondary storage. Secondary storage consists of devices, such as diskettes, which tin store information and programs outside the figurer itself. These devices supplement the computer's memory, which, as nosotros volition see, can concur data and programs merely temporarily.
Now let us consider the equipment related to these four aspects of data treatment in terms of what y'all would find on a personal computer.
Your Personal Calculator Hardware
Let us wait at the hardware in terms of a personal computer. Suppose yous want to do word processing on a personal computer, using the hardware shown in Effigy 1.
 |
Now we will take a general tour of the hardware needed for input, processing, output, and storage. These same components make up all computer systems, whether small-scale, medium, or large. In this discussion we volition effort to emphasize the types of hardware you are likely to have seen in your own surround. These topics will be covered in detail in after chapters.
Input: What Goes In
Input is the data that you put into the computer organization for processing. Here are some common ways of feeding input data into the system:- Typing on a keyboard. Computer keyboards operate in much the aforementioned mode as electric typewriter keyboards. The figurer responds to what y'all enter; that is, it "echoes" what you type past displaying it on the screen in front of you.
- Pointing with a mouse. A mouse is a device that is moved past hand over a flat surface. Every bit the brawl on its underside rotates, the mouse move causes corresponding movement of a arrow on the computer screen. Pressing buttons on the mouse lets you invoke commands.
- Scanning with a flatbed scanner, wand reader or bar code reader (Figure 3).
Flatbed scanners human activity like a copying automobile by using lite beams to scan a document or motion picture that is laid upon its glass confront. A keen way to ship pictures through email! Bar scanners, which y'all take seen in retail stores, utilise light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation beams to read special messages, numbers, or symbols such equally the zebra-striped bar codes on many products.
Effigy 3: Flatbed Scanner
The Processor and Memory: Data Manipulation
In a computer the processor is the center of activity. The processor, as we noted, is also called the central processing unit (CPU). The key processing unit of measurement consists of electronic circuits that interpret and execute program instructions, also as communicate with the input, output, and storage devices.
It is the key processing unit of measurement that actually transforms information into information. Information is the raw material to be processed by a computer. Such material can be letters, numbers, or facts like grades in a class, baseball batting averages, or lite and dark areas in a photograph. Processed data becomes information, information that is organized, meaningful, and useful. In school, for instance, an instructor could enter various student grades (data), which tin can exist processed to produce final grades and possibly a class boilerplate (information). Data that is peradventure uninteresting on its ain may become very interesting in one case it is converted to data. The raw facts (data) about your finances, such as a paycheck or a donation to charity or a medical bill may non exist captivating individually, simply together, these and other acts can be processed to produce the refund or corporeality you owe on your income taxation render (data).
Computer memory, also known as primary storage, is closely associated with the central processing unit of measurement only separate from it. Memory holds the data afterward it is input to the organization and before it is processed; likewise, memory holds the data later it has been candy but before it has been released to the output device. In add-on, memory holds the programs (computer instructions) needed past the central processing unit.
Output: What Comes Out
Output, the event produced past the central processing unit of measurement, is a computer's whole reason for being. Output is usable information; that is, raw input data that has been processed by the computer into data. The most common forms of output are words, numbers, and graphics. Word output, for example, may be the messages and memos prepared by office people using discussion processing software. Other workers may be more than interested in numbers, such equally those constitute in formulas, schedules, and budgets. In many cases numbers tin be understood more easily when output in the form of charts and graphics.The almost common output devices are reckoner screens (Figure iii)and printers (Figure 4). Screens can vary in their forms of display, producing text, numbers, symbols, art, photographs, and even video-in full color. Printers produce printed reports every bit instructed by a figurer program, oft in total color.
Y'all can produce output from a computer in other ways, including film and vox output. We volition examine all output methods in detail in a later chapter.
Secondary Storage
Secondary storage provides additional storage split up from memory. Secondary storage has several advantages. For example, it would exist unwise for a higher registrar to try to keep the grades of all the students in the college in the calculator's memory; if this were done, the reckoner would probably not have room to store anything else. Too, retentiveness holds data and programs only temporarily. Secondary storage is needed for big volumes of data and also for data that must persist after the estimator is turned off.The 2 near mutual secondary storage mediums are magnetic disk and magnetic tape. A magnetic disk can be a diskette or a hard disk. A diskette is usually iii-one/2 inches in diameter (in some rare cases older disks are 5-1/4 inches). A diskette is removable and then you lot can accept your data with you lot. Hard disks, shown in Effigy 5, have more than storage chapters than diskettes and also offer faster access to the data they concord. Hard disks are often contained in deejay packs shown in Figure half dozen that is built into the computer and so your data stays with the computer. Disk data is read by disk drives. Personal computer disk drives read diskettes; most personal computers also have hd drives. Mod personal computers are starting to come with removable storage media, like Cypher disks. These disks are slightly larger than a diskette and can exist inserted and removed similar a diskette, but concur much more information than a diskette and are faster for the CPU to access than a diskette. Most modernistic computers besides come with a CD-ROM drive. A CD is an optical deejay, it uses a laser beam to read the disk. CD's are removable and store big volumes of information relatively inexpensively. Some CD drives are read simply retention (ROM), which means that your reckoner can read programs from CD's, simply you can not save information to the CD yourself. Recently CD-RW drives and disks have become widely bachelor that allow you to create your own CDs by "writing" information such as music and photos to the CD.
Magnetic tape, which comes on a reel or cartridge shown in Effigy 7,
 |
| Figure 7: Magnetic Record |
We will report storage media in a subsequently part of the course.
The Complete Hardware System
The hardware devices attached to the computer are called peripheral equipment. Peripheral equipment includes all input, output, and secondary storage devices. In the case of personal computers, some of the input, output, and storage devices are built into the same physical unit of measurement. In many personal computers, the CPU and disk bulldoze are all independent in the aforementioned housing; the keyboard, mouse, and screen are separate.In larger calculator systems, however, the input, processing, output, and storage functions may be in split rooms, separate buildings, or even separate countries. For example, data may exist input on terminals at a branch bank then transmitted to the cardinal processing unit of measurement at the headquarters depository financial institution. The information produced by the central processing unit of measurement may then exist transmitted to the international offices, where it is printed out. Meanwhile, disks with stored data may exist kept in depository financial institution headquarters and indistinguishable data kept on deejay or record in a warehouse beyond boondocks for safekeeping.
Although the equipment may vary widely, from the simplest computer to the most powerful, generally the 4 elements of a computer system remain the same: input, processing, output, and storage. Now allow us await at the manner computers have been traditionally classified.
Classification of Computers
Computers come in sizes from tiny to monstrous, in both advent and ability. The size of a reckoner that a person or an organisation needs depends on the computing requirements. Clearly, the National Weather Service, keeping watch on the weather condition fronts of many continents, has requirements dissimilar from those of a car dealer's service department that is trying to continue runway of its parts inventory. And the requirements of both of them are different from the needs of a salesperson using a minor laptop reckoner to record customer orders on a sales trip. Supercomputers
The mightiest computers-and, of course, the about expensive-are known every bit supercomputers (Figure 1-6a). Supercomputers process billions of instructions per second. Most people do not have a straight need for the speed and power of a supercomputer. In fact, for many years supercomputer customers were an exclusive group: agencies of the federal government. The federal authorities uses supercomputers for tasks that require mammoth information manipulation, such as worldwide weather condition forecasting and weapons enquiry. But at present supercomputers are moving toward the mainstream, for activities as varied as stock analysis, car design, special effects for movies, and even sophisticated artworks (Figure one-7).
Mainframes
In the jargon of the computer merchandise, large computers are chosen mainframes. Mainframes are capable of processing data at very high speeds-millions of instructions per second-and have admission to billions of characters of data. The price of these large systems tin vary from several hundred thousand to many millions of dollars. With that kind of price tag, you will not buy a mainframe for merely any purpose. Their principal use is for processing vast amounts of data speedily, so some of the obvious customers are banks, insurance companies, and manufacturers. But this list is non all-inclusive; other types of customers are large mail-order houses, airlines with sophisticated reservation systems, government accounting services, aerospace companies doing circuitous shipping design, and the like. In the 1960s and 1970s mainframes dominated the computer mural. The 80s and early 90s had many people predicting that, with the appearance of very powerful and affordable personal computers, that mainframes would become extinct like the huge dinosaurs in nature'south progression. However, with the incredible explosion of the Internet in the mid 90s, mainframes may have been reborn. The electric current World wide web is based on the customer/server paradigm, where servers on the Internet, like LL Bean's Web Server, provide services, similar online shopping, to millions of people using personal computers as clients. The capacity required of these servers may be what saves the mainframe! Personal Computers
Personal computers are often called PCs. They range in price from a few hundred dollars to a few thousand dollars while providing more calculating ability than mainframes of the 1970s that filled entire rooms. A PC usually comes with a tower that holds the main circuit boards and disk drives of the calculator, and a collection of peripherals, such as a keyboard, mouse, and monitor.
In the new millennium there are ii chief kinds of PCs: the Apple Macintosh line, and "all of the others". The term "PC" or "IBM" refers to "all of the others", which is a historical artifact back to the days when IBM and Apple were the two primary competitors in the market place and IBM chosen its automobile a "personal computer". So, although a Macintosh is a personal computer, the term "PC" often ways a machine other than a Macintosh.
Macintoshes and PCs, in general, can not run software that was made for the other, without some special technology added to them. They run on dissimilar microprocessors. A PC is based on a microprocessor originally fabricated by the Intel company (such as Intel's Pentium, although other companies such as AMD now make "Pentium clones" that can run PC software.). Macintoshes use a PowerPC processor, or on older Macintoshes a processor made by Motorola. Besides, the operating organisation software that runs the two kinds of computers is unlike. PCs normally apply an Operating Organization made by Microsoft, like Windows98 or Windows2000. Macintoshes apply a different operating system, called MacOS, made by Apple tree. There are efforts to make the two kinds of computers compatible. Every bit Apple continues to lose its share of the market, Apple has the incentive to either join the rest or disappear.
 |
| Figure ten: Notebook Computer |
A computer that fits in a briefcase? A computer that weighs less than a newborn babe? A estimator y'all do not have to plug in? A calculator to use on your lap on an airplane? Yes, to all these questions. Notebook computers, also known equally Laptop computers, are wonderfully portable and functional, and popular with travelers who demand a computer that can go with them. Most notebooks accept diskettes or network connections, so it is easy to move information from 1 computer to another. Notebooks are not equally inexpensive as their size might suggest; many carry a price tag equivalent to a full-size personal computer for business. They typically accept almost as much computer capacity in terms of speed and storage. They practice not offer the full expandability for supporting peripherals as a personal estimator. For instance a MIDI estimator music keyboard may not be adaptable to a notebook reckoner. However, more and more peripherals are providing connectivity to laptops through a applied science called PCMCIA which allows peripherals to exist plugged into notebook computers through credit card sized cards that easily sideslip into the side of a notebook computer. Normal sized PCs are however more powerful, flexible, and cheaper, but notebooks are condign more competitive every solar day.
 |
| Figure eleven: Handheld Computer |
Using a pen-like stylus, pen-based computers accept handwritten input directly on a screen. Users of the handheld pen-based computers, also called personal digital assistants (PDA), like the Palm, enjoy having applications such as calendars, accost books, and games readily available. Recent PDA's offer Internet access, email, and cellular telephoning.
Internet and Networking
The Net is the well-nigh widely recognized and used form of computer network . Networks connect computers to each other to allow communication and sharing of services. Originally, a computer user kept all the calculator hardware in one place; that is, it was centralized in one room. Anyone wanting computer access had to go to where the estimator was located. Although this is still sometimes the case, most computer systems are decentralized. That is, the computer itself and some storage devices may be in ane place, but the devices to access the computer-terminals or fifty-fifty other computers-are scattered amidst the users. These devices are usually connected to the computer by telephone lines. For case, the computer and storage that has the data on your checking account may be located in banking company headquarters. but the terminals are located in branch banks all over boondocks and then a teller in any branch can discover out what your rest is. The subject of decentralization is intimately tied to information communications, the process of exchanging data over communications facilities, such as the telephone.
A network uses communications equipment to connect computers and their resources. In one type of network, a local area network (LAN), personal computers in an office are hooked together and so that users tin can communicate with each other. Users can operate their personal computers independently or in cooperation with other PCs or mainframes to exchange data and share resources. We discuss computer networks in item in a afterwards chapter.
Software: Telling the Car What to Do
In the by, when people thought nigh computers, they idea about machines. The borer on the keyboard, the clacking of the printers, the rumble of whirling disk drives, the changing flashes of color on a computer screen-these are the attention-getters. However, it is actually the software- the planned, step-by-pace instructions required to plow information into data-that makes a computer useful.
Categories of Software.
Mostly speaking, software can be categorized as system software or applications software. A subset of system software is an operating system, the underlying software found on all computers. Applications software, software that is applied, can be used to solve a particular problem or to perform a particular job. Applications software may be either custom or packaged. Many large organizations pay programmers to write custom software, software that is specifically tailored to their needs. We will use several forms of system software (e.g. Windows 2000, MacOS) and several application software programs (east.1000. Word, Excel, PowerPoint) in this class.
Some Task-Oriented Software. Word Processing/Desktop Publishing
Most users, whether at domicile or in concern, are drawn to task-oriented software, sometimes chosen productivity software, that can make their work faster and their lives easier. The collective ready of business tasks is limited, and the number of full general paths towards performing these tasks is limited, too. Thus, the tasks and the software solutions autumn, for the most part, into simply a few categories, which can be found in most business environments. These major categories are give-and-take processing (including desktop publishing), spreadsheets, database direction, graphics, and communications. We will present a brief description of each category here.
The near widely used personal estimator software is word processing software. This software lets yous create, edit, format, store, and print text and graphics in one document. In this definition it is the three words in the heart-edit, format, and store-that reveal the divergence betwixt word processing and plain typing. Since you can store the memo or certificate you lot type on disk, you tin retrieve information technology another fourth dimension, modify it, reprint it, or practice whatever you like with it. You can see what a great time-saver word processing can be: unchanged parts of the stored document do not need to be retyped; the whole revised document can he reprinted as if new.
Equally the number of features in word processing packages has grown, word processing has crossed the border into desktop publishing territory. Desktop publishing packages are commonly improve than word processing packages at meeting high-level publishing needs, especially when information technology comes to typesetting and color reproduction. Many magazines and newspapers today rely on desktop publishing software. Businesses use it to produce professional-looking newsletters, reports, and brochures-both to meliorate internal communication and to make a amend impression on the outside globe.
Electronic Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets, made up of columns and rows, have been used as business organisation tools for centuries (Figure 11). A manual spreadsheet can be tedious to ready and, when there are changes, a considerable amount of calculation may need to he redone. An electronic spreadsheet is all the same a spreadsheet, simply the reckoner does the work. In particular, spreadsheet software automatically recalculates the results when a number is changed. This capability lets business concern people try different combinations of numbers and obtain the results quickly. This ability to ask "What if . . . ?" helps business people make ameliorate, faster decisions. In this course, we apply Microsoft's Excel spreadsheet application software.
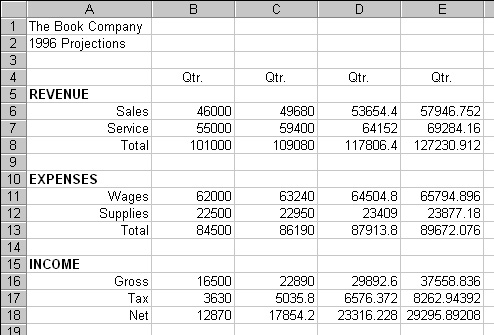 |
| Effigy 11: Spreadsheet Software |
Database Direction
Software used for database direction-the direction of a drove of interrelated facts-handles data in several means. The software can store information, update it, manipulate it, written report information technology in a variety of views, and print it in as many forms. By the time the data is in the reporting stage-given to a user in a useful grade-information technology has become information. A concert promoter, for instance, can store and change data about upcoming concert dates, seating, ticket prices, and sales. Later this is done, the promoter tin can use the software to recollect information, such as the number of tickets sold in each price range or the percentage of tickets sold the day earlier the concert. Database software can be useful for anyone who must go on track of a big number of facts. Database software is shown in Figure 12.
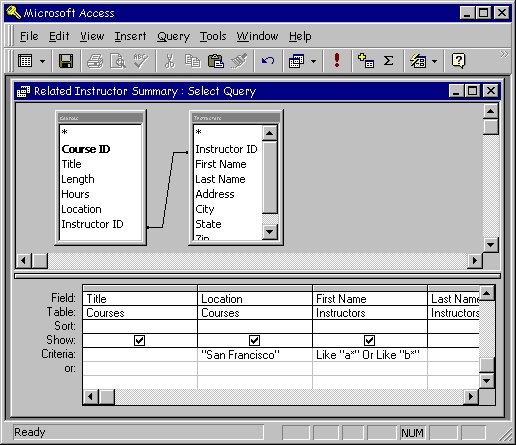 |
| Figure 12: Database Software |
Graphics
It might seem wasteful to show graphics to business people when standard calculator printouts are readily bachelor. All the same, graphics, maps, and charts can assist people compare data and spot trends more easily, and make decisions more quickly. In addition, visual data is usually more than compelling than a page of numbers. We utilize Microsoft's PowerPoint and Adobe's Photoshop application software for graphics. We use it in two ways: for doing original drawings, and for creating visual aids to projection as a support to an oral presentation.
Communications
We have already described communications in a full general way. From the viewpoint of a worker with a personal figurer at habitation, communications means-in unproblematic terms-that he or she can hook a phone upwards to the calculator and communicate with the calculator at the office, or get at data stored in someone else'southward computer in some other location. Nosotros use Microsoft's Cyberspace Explorer awarding software for doing email, Www browsing, and participating in Internet discussion groups.
Source: https://homepage.cs.uri.edu/faculty/wolfe/book/Readings/Reading01.htm
Publicar un comentario for "what communicates with the computer and tells it what to do?"